Рекомендация: прочитайте задачу! Выполните ее и сравните полученный результат с картинкой CMD
Если вы полностью уверены что не можете осилить эту задачу, советую вам просмотреть код и полностью в нем разобраться! Протестировать все в отладчике!
Напишите программу, проверяющую число, введенное с клавиатуры на четность.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int numberN = 0; // UserInput
cout << "(integer) Enter the number: " << endl;
cin >> numberN;
numberN = numberN - ((numberN / 2) * 2); // % 2
numberN == 1 ? cout << "Not Even" << endl : cout << "Even" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int n = 0;
cout << "Enter a natural number < 100" << endl;
cin >> n;
if (n < 100) {
if (n >= 10) {
n = (n / 10) + (n % 10);
cout << "You entered the number of digits = " << '2' << " Sum = " << n << endl;
}
else
cout << "You entered the number of digits = " << '1' << " Sum = " << n << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Maximum 99 " << endl;
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
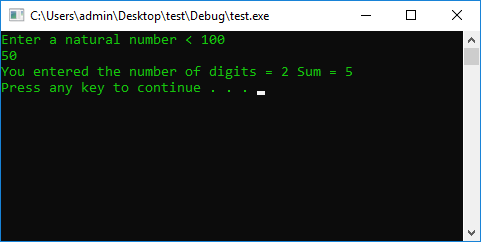
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int code = 0;
double TimeCall = 0;
cout << endl;
cout << " Enter the operator code \n"
<< "---------------------------------------------------\n"
<< "| Mobile operators | Code | Price per minute, UAH |\n"
<< "---------------------------------------------------\n"
<< "| Kyivstar | 67 | 3,00 |\n"
<< "---------------------------------------------------\n"
<< "| Life | 66 | 2.50 |\n"
<< "---------------------------------------------------\n"
<< "| Vodafone | 63 | 2.00 |\n"
<< "---------------------------------------------------\n";
cout << endl;
cin >> code;
cout << "Enter the number of minutes" << endl;
cin >> TimeCall;
switch (code)
{
case 67: {
cout << "<< Kyivstar >> Call cost = " << TimeCall * 3.00 << " UAH" << endl;
break;
}
case 66: {
cout << "<< Life >> Call cost = " << TimeCall * 2.50 << " UAH" << endl;
break;
}
case 63: {
cout << "<< Vodafone >> Call cost = " << TimeCall * 2.00 << " UAH" << endl;
break;
}
default: {
cout << "*** Input error ***" << endl;
break;
}
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
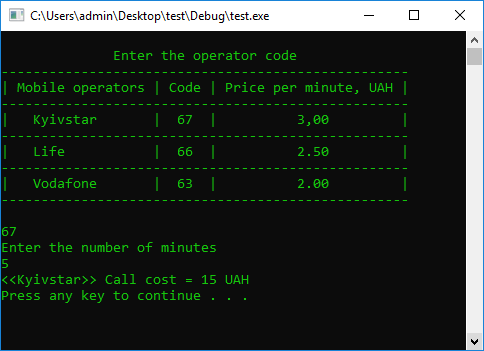
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
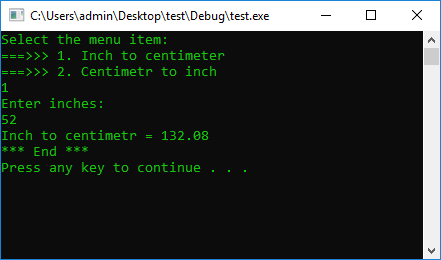
const double inch = 2.54;
double UserInput = 0;
cout << "Select the menu item: \n"
<< "===>>> 1. Inch to centimeter\n"
<< "===>>> 2. Centimetr to inch" << endl;
cin >> UserInput;
if (UserInput == 1) {
UserInput = 0;
cout << "Enter inches: " << endl;
cin >> UserInput;
UserInput = UserInput * inch;
cout << "Inch to centimetr = " << UserInput << endl;
}
if (UserInput == 2) {
UserInput = 0;
cout << "Enter centimetrs: " << endl;
cin >> UserInput;
UserInput = UserInput / inch;
cout << "In inches = " << UserInput << endl;
}
else
cout << "*** End ***" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
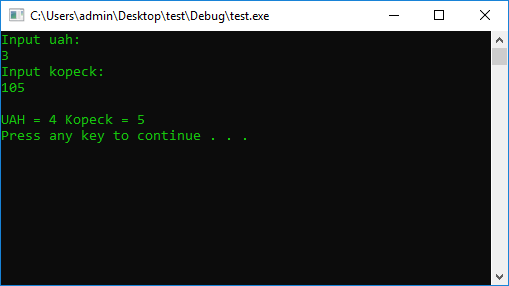
int uah = 0, kopeck = 0;
cout << "Input uah: " << endl;
cin >> uah;// User input uah
cout << "Input kopeck: " << endl;
cin >> kopeck; // User input kopeck
cout << endl;
uah = (uah * 100) + kopeck; // All in one number (UAH = Kopeck)
cout << "UAH = " << uah / 100 << " Kopeck = " << uah % 100 << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
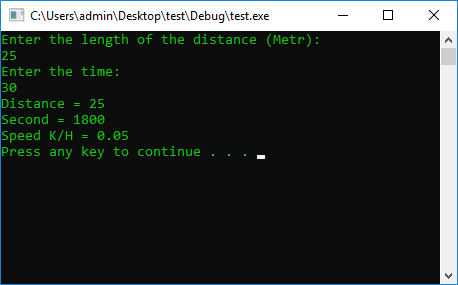
double S = 0, T = 0, sum = 0;
int timeX = 0, timeY = 0;
cout << "Enter the length of the distance (Metr): " << endl;
cin >> S;
cout << "Enter the time: " << endl;
cin >> T;
cout << "Distance = " << S << endl;
timeX = T; // We take the whole part
timeY = ((T - timeX) * 100); //We take the right-hand side of the variable
timeX = (timeY % 1000) + (timeX * 60);
cout << "Second = " << timeX << endl;
sum = S / (timeX / 3.600);// //We work by formula
cout.precision(4);//Number of signs
cout << "Speed K/H = " << sum << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
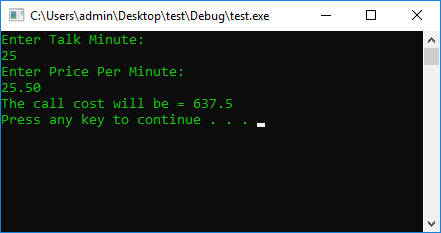
double PricePerMinute = 0, TalkTime = 0, PricePerSecond = 0, Sum = 0;
int second = 0;
cout << "Enter Talk Minute: " << endl;
cin >> TalkTime;
cout << "Enter Price Per Minute: " << endl;
cin >> PricePerMinute;
PricePerSecond = PricePerMinute / 60;
second = TalkTime; // We take the whole part
Sum = ((TalkTime - second) * 100) + (second * 60) * PricePerSecond; // //We take the right-hand side of the variable + Logic of calculation
cout.precision(4);//Number of signs
cout << "The call cost will be = " << Sum << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
const int FuelPrice = 165;
const int liter = 10;
double V = 0, t = 0, S = 0, PriseLitr = 0;
int Integer = 0;
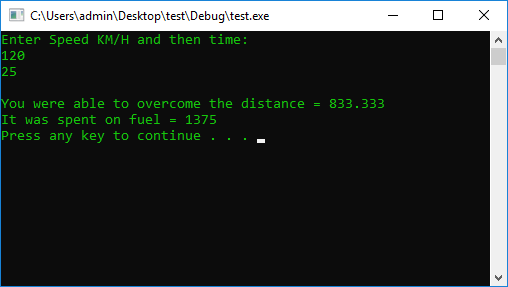
cout << "Enter Speed KM/H and then time: " << endl;
cin >> V >> t;
PriseLitr = FuelPrice;
PriseLitr = PriseLitr / 100;
Integer = V;
V = ((V - Integer) * 100);// I take the whole part + Create the whole part
Integer = (Integer * 1000) + (V * liter);
S = (((double)Integer / 3600) * t);//We work by formula
cout << endl;
cout << "You were able to overcome the distance = " << S << endl;
cout << "It was spent on fuel = " << S * PriseLitr << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
//Storage Numbers = a b c
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
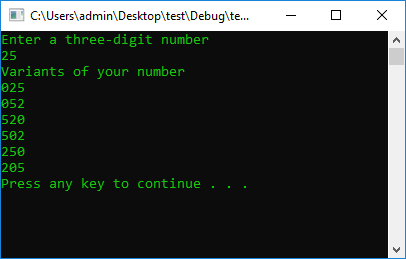
cout << "Enter a three-digit number" << endl;
cin >> a;
b = a;
c = b;
a = a / 100;
b = (b / 10) % 10;
c = c % 10;
cout << "Variants of your number" << endl;
cout << a << b << c << "\n" << a << c << b << "\n" << c << b << a << "\n"
<< c << a << b << "\n" << b << c << a << "\n" << b << a << c << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int Number = 0;
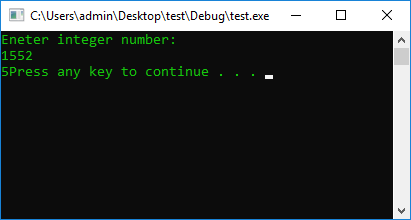
cout << "Eneter integer number: " << endl;
cin >> Number;
Number = (Number / 100) % 10; // We get rid of hundreds and tens
cout << Number;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int a = 0;
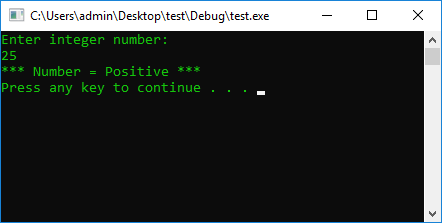
cout << "Enter integer number: " << endl;
cin >> a;
if (a > 0) {
cout << "*** Number = Positive ***" << endl;
}
else
cout << "*** Number = Negative ***" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
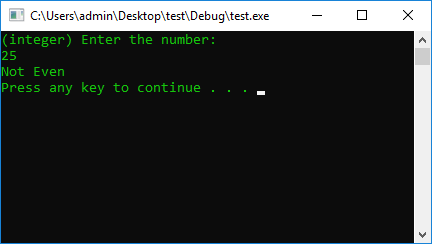
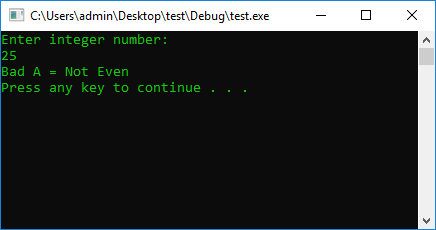
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int a = 0;
cout << "Enter integer number: " << endl;
cin >> a;
if (a % 2 == 0) {
cout << "Good A = Even" << endl;
}
else
cout << "Bad A = Not Even" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
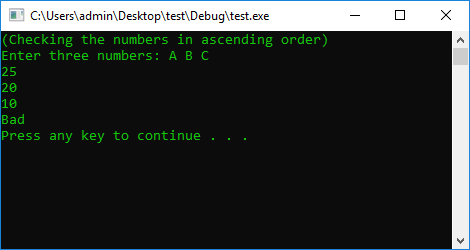
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int a, b, c;
cout << "(Checking the numbers in ascending order)\nEnter three numbers: A B C " << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a < b && b < c) {
cout << "Good" << endl;
}
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
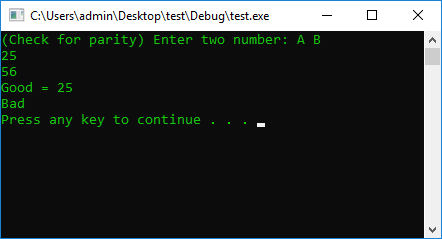
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int A = 0, B = 0;
cout << "(Check for parity) Enter two number: A B" << endl;
cin >> A >> B;
if (A % 2 == 1) {
cout << "Good = " << A << endl;
}
if (B % 2 == 1) {
cout << "Good = " << B << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Bad" << endl;
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
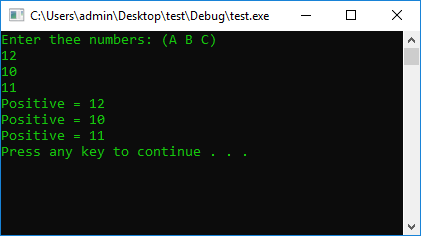
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
cout << "Enter thee numbers: (A B C)" << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a > 0) {
cout << "Positive = " << a << endl;
}
if (b > 0) {
cout << "Positive = " << b << endl;
}
if (c > 0) {
cout << "Positive = " << c << endl;
}
else
cout << "Negative" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int Number = 0;
cout << "Enter integer number: (Cheking Eleven + Two-valued)" << endl;
cin >> Number;
if (Number % 2 == 0) {
if (Number >= 10) {
cout << "Good = Eleven + Two-valued" << endl;
}
}
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
cout << "Enter thee numbers: (A B C)" << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a == b || b == a) {
cout << "A and B are the same" << endl;
}
if (a == c || c == a) {
cout << "A and C are the same" << endl;
}
if (b == c || c == b) {
cout << "B and C are the same" << endl;
}
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
cout << "Enter thee numbers: (A B C)" << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a != b && b != a && b != c && c != a)
cout << "All numbers are different" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
cout << "Enter thee numbers: (A B C)" << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a < b && a < c && b < c)
cout << "Ascending Numbers" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, y = 0;
cout << "Enter the quarter's coordinates: (X Y)" << endl;
cin >> x >> y;
if (y > 0 && x < 0)
cout << "II Coordinate Quarter" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
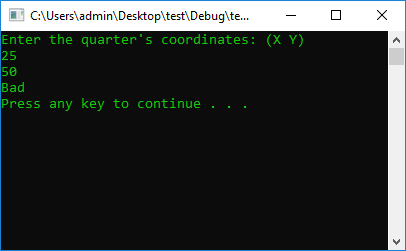
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, y = 0;
cout << "Enter the quarter's coordinates: (X Y)" << endl;
cin >> x >> y;
if (y < 0 && x > 0)
cout << "IV Coordinate Quarter" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
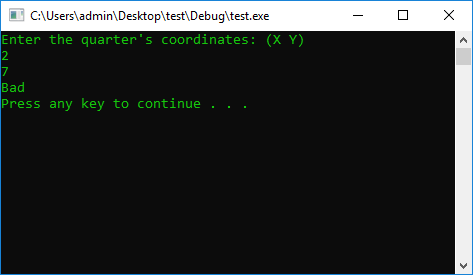
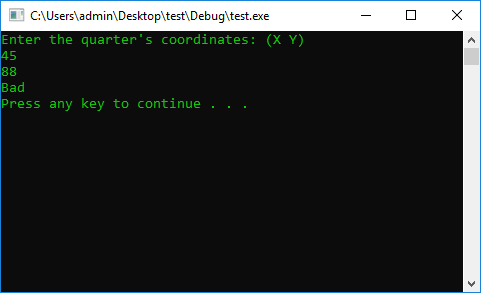
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, y = 0;
cout << "Enter the quarter's coordinates: (X Y)" << endl;
cin >> x >> y;
if (y > 0 && x < 0 || y < 0 && x < 0)
cout << "(II || III) Coordinate Quarter" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
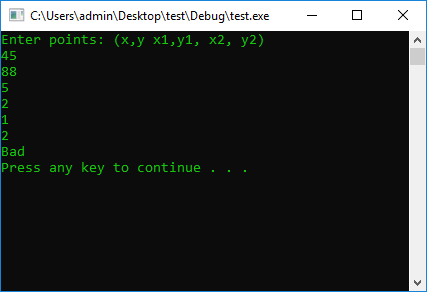
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, y = 0, x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0;
cout << "Enter points: (x,y x1,y1, x2, y2)" << endl;
cin >> x >> y >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
if ((y < y1) && (y > y2) && (x > x1) && (x < x2))
cout << "Good" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
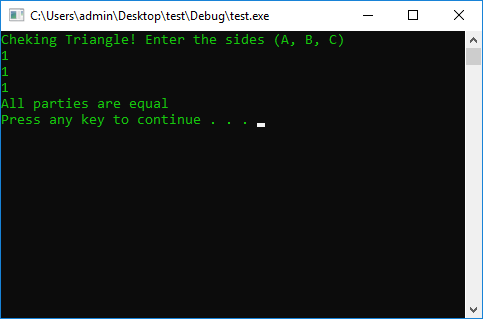
COLOR_CMD
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
cout << "Cheking Triangle! Enter the sides (A, B, C)" << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a == c && a == b || b == c && b == a || c == b && c == a)
cout << "All parties are equal" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
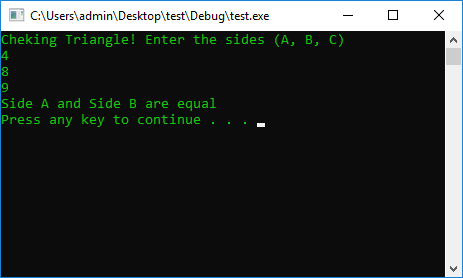
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
cout << "Cheking Triangle! Enter the sides (A, B, C)" << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a != c && a == b || b != c && b == a || c != b && c != a)
cout << "Side A and Side B are equal" << endl;
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
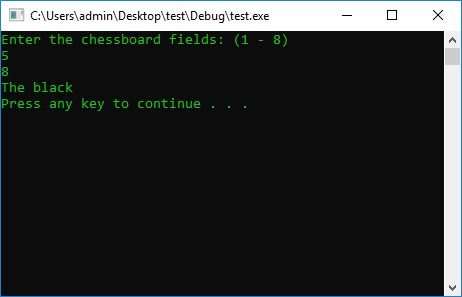
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, y = 0;
cout << "Enter the chessboard fields: (1 - 8)" << endl;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x > 8 || y > 8) {
cout << "x || y > 8 (ERROR)" << endl;
}
if ((x + y) % 2 == 1 || x == 1 && y == 1) { // The board is arranged according to the scheme White Even Black is not even
cout << "The black" << endl;
}
else
cout << "The white" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
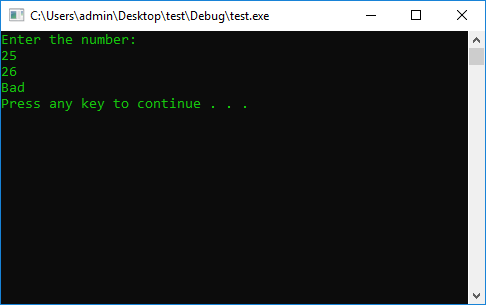
int n = 0;
cout << "Enter the number: " << endl;
cin >> n;
if (n > 0) {
n++;
cout << n << endl;
}
if (n < 0) {
n += 2;
cout << n << endl;
}
if (n == 0) {
n += 10;
cout << n << endl;
}
else
cout << "Bad" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, y = 0;
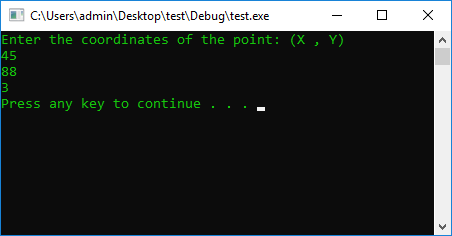
cout << "Enter the coordinates of the point: (X , Y)" << endl;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x == 0 && y == 0)
cout << 0 << endl;
if (x != 0 && y == 0)
cout << 1 << endl;
if (x == 0 && y != 0)
cout << 2 << endl;
else
cout << 3 << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, x1 = 0, x2 = 0, x3 = 0, y = 0, y1 = 0, y2 = 0, y3 = 0;
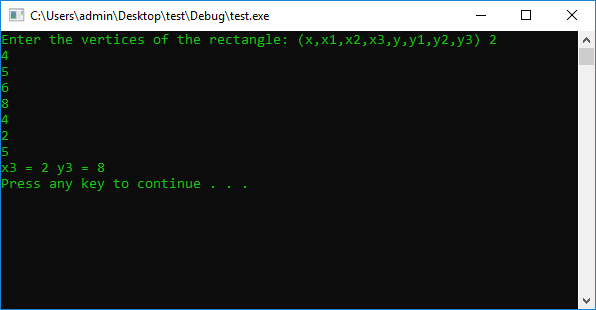
cout << "Enter the vertices of the rectangle: (x,x1,x2,x3,y,y1,y2,y3) ";
cin >> x >> x1 >> x2 >> x3 >> y >> y1 >> y2 >> y3;
if (x == x)
x3 = x2;
if (x == x2)
x3 = x1;
else
x3 = x;
if (y == y1)
y3 = y2;
if (y == y2)
y3 = y1;
else
y3 = y;
cout << "x3 = " << x3 << " y3 = " << y3 << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int InputUser = 0;
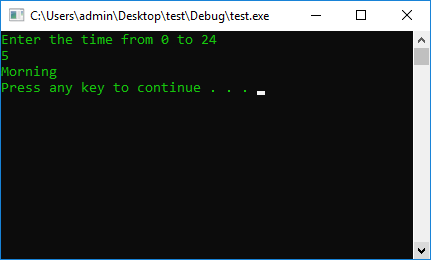
cout << "Enter the time from 0 to 24" << endl;
cin >> InputUser;
switch (InputUser)
{
case 0: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
case 1: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
case 2: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
case 3: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
case 4: {
cout << "Morning" << endl;
break;
}
case 5: {
cout << "Morning" << endl;
break;
}
case 6: {
cout << "Morning" << endl;
break;
}
case 7: {
cout << "Morning" << endl;
break;
}
case 8: {
cout << "Morning" << endl;
break;
}
case 9: {
cout << "Morning" << endl;
break;
}
case 10: {
cout << "day" << endl;
break;
}
case 11: {
cout << "day" << endl;
break;
}
case 12: {
cout << "Noon" << endl;
break;
}
case 13: {
cout << "day" << endl;
break;
}
case 14: {
cout << "day" << endl;
break;
}
case 15: {
cout << "day" << endl;
break;
}
case 16: {
cout << "evening" << endl;
break;
}
case 17: {
cout << "evening" << endl;
break;
}
case 18: {
cout << "evening" << endl;
break;
}
case 19: {
cout << "evening" << endl;
break;
}
case 20: {
cout << "evening" << endl;
break;
}
case 21: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
case 22: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
case 23: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
case 24: {
cout << "night" << endl;
break;
}
default: {
cout << "Error" << endl;
break;
}
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
char InputUser;
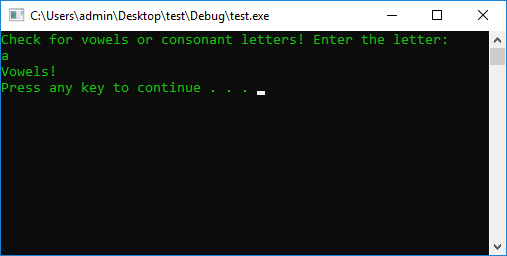
cout << "Check for vowels or consonant letters! Enter the letter: " << endl;
cin >> InputUser;
switch (InputUser) {
case 'A':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'E':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'I':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'O':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'U':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'Y':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
case 'a':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'e':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'i':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'o':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'u':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
case 'y':
cout << "Vowels!" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "Consonant!" << endl;
break;
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
char UserInput;
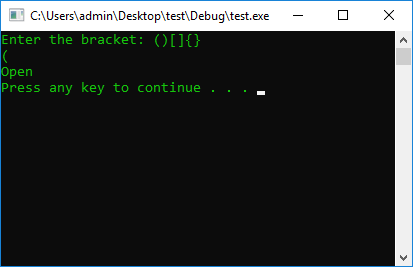
cout << "Enter the bracket: ()[]{}" << endl;
cin >> UserInput;
switch (UserInput)
{
case '(': {
cout << "Open" << endl;
break;
}
case '[': {
cout << "Open" << endl;
break;
}
case '{': {
cout << "Open" << endl;
break;
}
default:
cout << "Closed" << endl;
break;
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
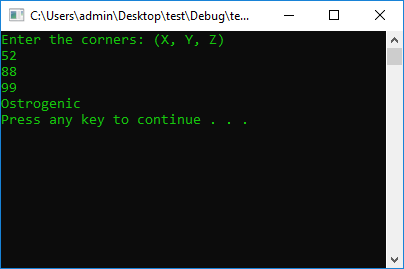
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int x = 0, y = 0, z = 0;
cout << "Enter the corners: (X, Y, Z)" << endl;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
if (x > 90 && y > 90 && z > 90)
cout << "Obtuse" << endl;
if (x == 90 && y == 90 && z == 90)
cout << "Rectangular" << endl;
else
cout << "Ostrogenic" << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
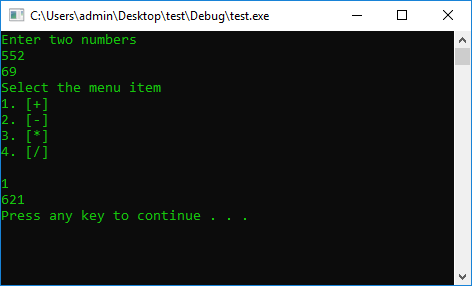
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int A = 0, B = 0, N = 0;
cout << "Enter two numbers" << endl;
cin >> A >> B;
cout << "Select the menu item\n"
<< "1. [+]\n"
<< "2. [-]\n"
<< "3. [*]\n"
<< "4. [/]\n" << endl;
cin >> N;
switch (N)
{
case 1: {
cout << A + B << endl;
break;
}
case 2: {
cout << A - B << endl;
break;
}
case 3: {
cout << A * B << endl;
break;
case 4: {
if (A != 0) {
cout << A / B << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "A == 0 (ERROR)" << endl;
}
break;
}
}
default:
cout << "Bad" << endl;
break;
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
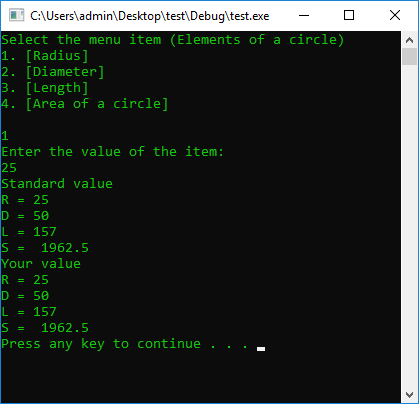
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
const double Pi = 3.14;
double R = 0, D = 0, L = 0, S = 0, item = 0;
int N = 0;
cout << "Select the menu item (Elements of a circle)\n"
<< "1. [Radius]\n"
<< "2. [Diameter]\n"
<< "3. [Length]\n"
<< "4. [Area of a circle]\n" << endl;
cin >> N;
cout << "Enter the value of the item: " << endl;
cin >> item;
switch (N)
{
case 1: {
cout << "Standard value" << endl;
R = item;
D = R * 2;
L = (Pi * 2) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
cout << "Your value" << endl;
R = item;
D = 2 * R;
L = (2 * Pi) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
break;
}
case 2: {
cout << "Standard value" << endl;
R = item;
D = R * 2;
L = (Pi * 2) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
cout << "Your value" << endl;
R = item * 2;
D = R * 2;
L = (Pi * 2) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
break;
}
case 3: {
cout << "Standard value" << endl;
R = item;
D = R * 2;
L = (Pi * 2) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
cout << "Your value" << endl;
R = (Pi * 2) * item;
D = R * 2;
L = (Pi * 2) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
break;
}
case 4: {
cout << "Standard value" << endl;
R = item;
D = R * 2;
L = (Pi * 2) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
cout << "Your value" << endl;
R = (item * item) * Pi;
D = R * 2;
L = (Pi * 2) * R;
S = (R * R) * Pi;
cout << "R = " << R << endl;
cout << "D = " << D << endl;
cout << "L = " << L << endl;
cout << "S = " << S << endl;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
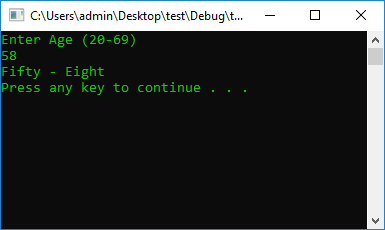
int Age = 0, Storage = 0;
cout << "Enter Age (20-69)" << endl;
cin >> Age;
Storage = Age;
Age = Age % 10; ////Struggling with cases :-)
Age = Storage - Age;
Storage = Storage - Age;
switch (Age)
{
case 20: {
cout << "Twenty - ";
break;
}
case 30: {
cout << "Thirty - ";
break;
}
case 40: {
cout << "Forty - ";
break;
}
case 50: {
cout << "Fifty - ";
break;
}
case 60: {
cout << "Sixty - ";
break;
}
default:
cout << "20-69" << endl;
break;
}
switch (Storage)
{
case 1: {
cout << "One" << endl;
break;
}
case 2: {
cout << "Two" << endl;
break;
}
case 3: {
cout << "Three" << endl;
break;
}
case 4: {
cout << "Four" << endl;
break;
}
case 5: {
cout << "Five" << endl;
break;
}
case 6: {
cout << "Six" << endl;
break;
}
case 7: {
cout << "Seven" << endl;
break;
}
case 8: {
cout << "Eight" << endl;
break;
}
case 9: {
cout << "Nine" << endl;
break;
}
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
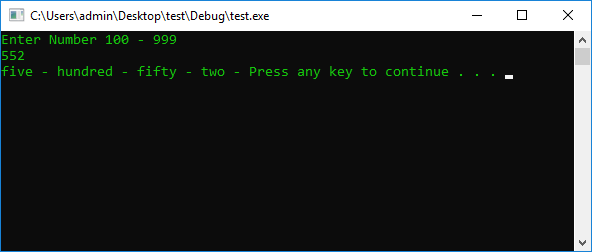
int Number = 0, Storage1 = 0, Storage2 = 0, Storage3 = 0, Storage4 = 0;
cout << "Enter Number 100 - 999" << endl;
cin >> Number;
Storage1 = Number % 100; // 100
Storage2 = (Number / 10) % 100; // 10
Storage3 = Number % 10; // 1
Storage2 = Storage1 - Storage3;
Storage1 = Number - Storage1;
Number = Number - Storage1;
if (Number >= 10 && Number <= 19) { // Validation of such numbers as for example 211
Storage4 = (Number % 10) + 10;
Storage3 = 0;
}
switch (Storage1)
{
case 100: {
cout << "one - hundred - ";
break;
}
case 200: {
cout << "two - hundred - ";
break;
}
case 300: {
cout << "three - hundred - ";
break;
case 400: {
cout << "four - hundred - ";
break;
}
case 500: {
cout << "five - hundred - ";
break;
}
case 600: {
cout << "six - hundred - ";
break;
}
case 700: {
cout << "seven - hundred - ";
break;
}
case 800: {
cout << "eight - hundred - ";
break;
}
case 900: {
cout << "nine - hundred - ";
break;
}
}
default:
cout << "100-999" << endl;
break;
}
switch (Storage2)
{
case 20: {
cout << "twenty - ";
break;
}
case 30: {
cout << "thirty - ";
break;
}
case 40: {
cout << "forty - ";
break;
}
case 50: {
cout << "fifty - ";
break;
}
case 60: {
cout << "sixty - ";
break;
}
case 70: {
cout << "seventy - ";
break;
}
case 80: {
cout << "eighty - ";
break;
}
case 90: {
cout << "ninety - ";
break;
}
}
switch (Storage4)
{
case 10: {
cout << "ten - ";
break;
}
case 11: {
cout << "eleven - ";
break;
}
case 12: {
cout << "twelve - ";
break;
}
case 13: {
cout << "thirteen - ";
break;
}
case 14: {
cout << "fourteen - ";
break;
}
case 15: {
cout << "fifteen - ";
break;
}
case 16: {
cout << "sixteen - ";
break;
}
case 17: {
cout << "seventeen - ";
break;
}
case 18: {
cout << "eightteen - ";
break;
}
case 19: {
cout << "nineteen - ";
break;
}
}
switch (Storage3)
{
case 1: {
cout << "one - ";
break;
}
case 2: {
cout << "two - ";
break;
}
case 3: {
cout << "three - ";
break;
}
case 4: {
cout << "Four - ";
break;
}
case 5: {
cout << "five - ";
break;
}
case 6: {
cout << "six - ";
break;
}
case 7: {
cout << "seven - ";
break;
}
case 8: {
cout << "eight - ";
break;
}
case 9: {
cout << "nine - ";
break;
}
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
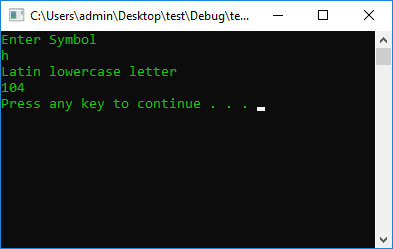
COLOR_CMD
char symbol;
int Checking = 0;
cout << "Enter Symbol" << endl;
cin >> symbol;
Checking = symbol;
if (Checking < 58 && Checking > 47) {
cout << "digit from 0 to 9" << endl;
}
if (Checking < 123 && Checking > 98) {
cout << "Latin lowercase letter" << endl;
}
if (Checking < 91 && Checking > 66) {
cout << "Latin capital letter" << endl;
}
else
cout << Checking << endl;
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}
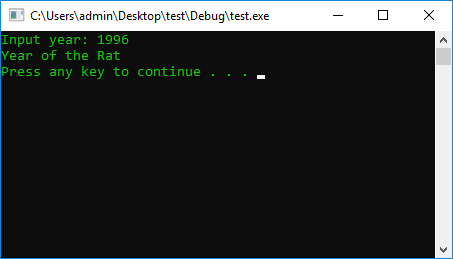
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define STOP_CMD system("pause");
#define COLOR_CMD system("color 0A");
int main() {
COLOR_CMD
int year = 0;
cout << "Input year: ";
cin >> year;
switch (year % 12)
{
case 0: {
cout << "Year of the Monkey" << endl;
break;
}
case 1: {
cout << "Year of the Rooster" << endl;
break;
}
case 2: {
cout << "Year of the Dog" << endl;
break;
}
case 3: {
cout << "Year of the Pig" << endl;
break;
}
case 4: {
cout << "Year of the Rat" << endl;
break;
}
case 5: {
cout << "Year of the Cow" << endl;
break;
}
case 6: {
cout << "Year of the Tiger" << endl;
break;
case 7: {
cout << "Year of the Hare" << endl;
break;
}
case 8: {
cout << "Year of the Dragon" << endl;
break;
}
case 9: {
cout << "The Year of the Snake" << endl;
break;
}
case 10: {
cout << "Year of the Horse" << endl;
break;
}
case 11: {
cout << "Year Sheep" << endl;
break;
}
default:
cout << "Year (ERROR)" << endl;
break;
}
}
STOP_CMD
return 0;
}